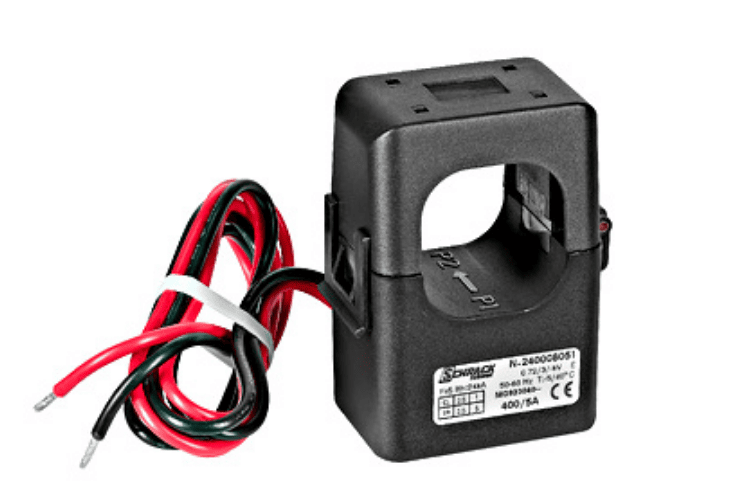
Current transformers play an important role in protecting electrical systems. They are primarily used where a current is too high to measure directly such as power plants, grid stations, etc. These transformers convert high alternating current into a smaller value that can be safely measured. If you want to start with more basics you can also check out our article on the basics of transformers and the different types of transformers, in this article, we will discuss the different types of current transformers.
Table of Contents
- What is a Current Transformer?
- Types of Current Transformers Based on Applications
- └ Metering Current Transformers
- └ Protection Current Transformers
- Current Transformer Types Based on Construction
- └ Bar-Type Current Transformers
- └ Cable-Type Current Transformers
- └ Bushing-Type Current Transformers
- └ Block-Type Current Transformers
- Current Transformer Types Based on Phases
- └ Single-Phase Current Transformers
- └ Three-Phase Current Transformers
- Current Transformer Types Based on Core Types
- └ Wound Core Current Transformers
- └ Toroidal (Ring) Core Current Transformers
- └ Split Core Current Transformers
What is a Current Transformer?
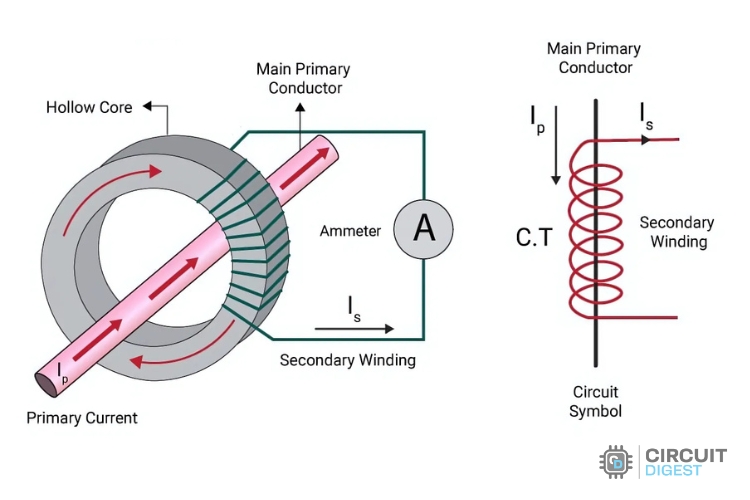
The current transformer is a step-down transformer, having primary and secondary windings without any electrical connection between them. The primary winding is directly connected in series with the high-current circuit. The secondary winding is connected to protective devices or measuring instruments, such as ammeters, relays, etc. They reduce the high alternating currents (AC) in the primary winding to lower value in the secondary winding. The current in the primary and secondary windings of current transformers are proportional to each other.

The primary winding of the transformer carries the full load current which needs to be measured, and the secondary winding carries the current proportional to the current in primary winding. The primary winding is connected to the main circuit and secondary winding is connected to the current windings of the instruments or meters. Both the windings are insulated from the cores and each other.
The following figure shows the construction and symbol of the current transformer.
Types of Current Transformers Based on Applications
Current transformers are categorized into two types based on their application:
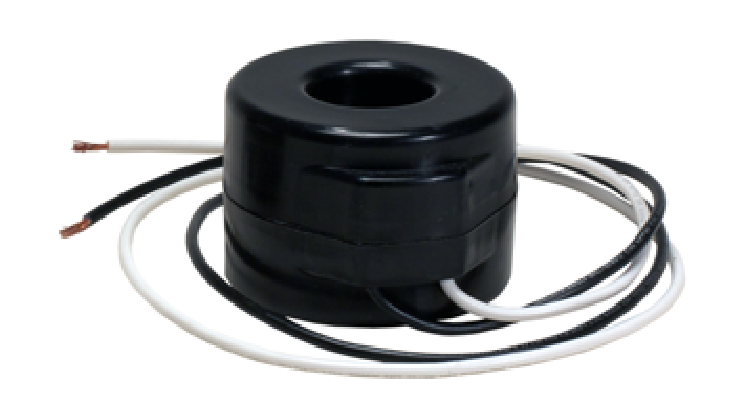
Metering Current Transformers
Metering Current Transformers are used for safe measurement of high currents. They are used with measuring instruments like voltmeters, ammeters or kilowatt-hour meters to measure current or total power being consumed. They are small in size and highly effective in measuring the electrical usage of any circuit in a residential building or any industrial facility for billing purpose.
These CTs are typically made from premium grade laminated silica steel cores. They are widely used in industrial-scale power systems and power grids.

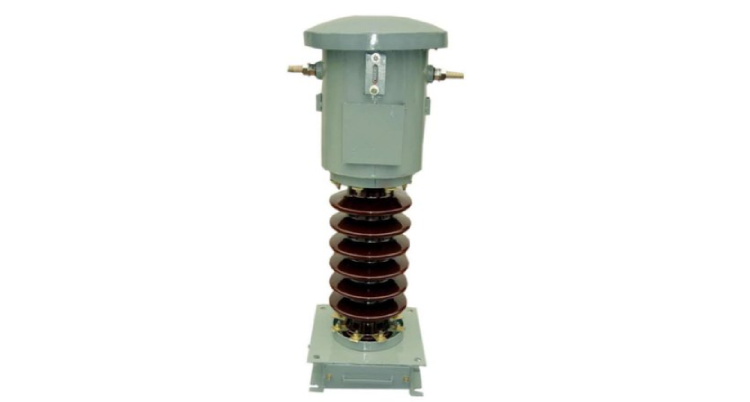
Protection Current Transformers
Protection Current Transformers are used to protect electrical circuits against overloading and short-circuits. They monitor and respond to fault conditions in electrical systems. Their secondary leads are connected to protective relays which are sensitive measuring instruments. These relays activate the protective device, causing it to trip when there is a short circuit in the circuit, caused by its overloading. In these transformers the core must be large enough to avoid saturation. That’s why these types of transformers are large in size.
These protection CTs are capable of handling high currents, often up to 10-20 times their rated current, during fault conditions. Their core is made of cold-rolled silicon steel, providing a high saturation point. It provides accurate performance even during high fault currents. These CTs prevent damage to equipment and maintain system stability. They are widely used in power plants and industrial setups.

Current Transformer Types Based on Construction
Current transformers (CTs) can be classified based on their construction, each having different design, installation, and operational suitability for specific applications. Below are the main types of CTs based on construction:
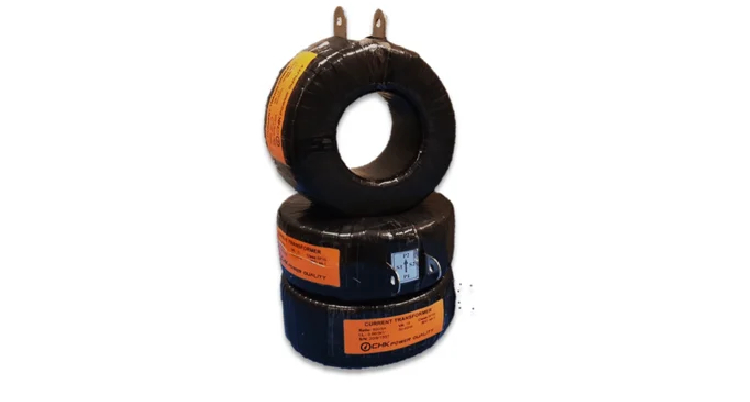
Bar-Type Current Transformers
Bar-type Current Transformers contain a solid bar placed permanently through the window. They are designed for mounting in-line with busbars. Their primary winding consists of a single-turn conductor which is a fully insulated bar. This insulation ensures safety of primary winding in high voltage levels. The secondary winding is wound around a laminated steel core.
Their robust construction enables them to withstand short circuit forces and mechanical stresses. These CTs are used in high-current applications such as power distribution systems, electrical substations, power generation plants, renewable energy systems, etc. They are commonly found in installations where the potential is equal or less than 25kV.

Cable-Type Current Transformers
Cable-Type Current Transformers converts high current into measurable values for meters, measuring and protection devices. They are designed to be installed on fully insulated medium and high voltage cables. These CTs are used in indoor switchgears and medium or high voltage outdoor systems.
In these transformers the primary conductor is the cable, which provides the insulation against high voltage. The transformer itself is installed on a frame over the cable. They are flexible and cost-effective, making them a great option for upgrading existing setups. These CTs are perfect for load analysis in commercial, residential, and industrial applications.

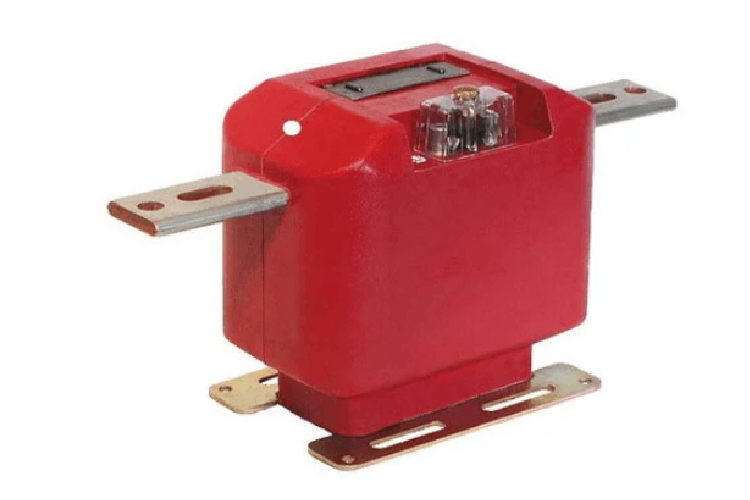
Bushing-Type Current Transformers
Bushing-Type CTs are designed for monitoring and protection in high-voltage systems. A bushing is an important component in transformers, enabling them to withstand mechanical, electrical, and environmental stresses. The CT’s core is housed within the bushing’s insulation, providing compactness and reducing space requirements.
These CTs are widely used in substations for accurate current measurement and protection. Their integration into bushings minimizes exposure to environmental factors, enhancing durability and reliability. They can be easily installed as opening the tank or removing bushings is not necessary for mounting. They are used in relaying and metering on circuit breakers or existing power transformers.

Block-Type Current Transformers
Block-Type CTs are compact and designed for confined spaces, such as control panels and distribution boards. Their block-shaped design allows easy installation in applications where space is limited. They are commonly used in low and medium-voltage applications for metering and protection. Despite their small size, they offer reliable performance and are suitable for current ratings within their specified range. They are used in industries where space-saving designs are critical. However their current-handling capacity may be limited compared to larger CTs.

Current Transformer Types Based on Phases
Current transformers (CTs) are categorized based on the number of phases they have. Below are the main types of CTs based on phases:
Single-Phase Current Transformers
Single-Phase Current Transformers work on a single-phase power supply. They have a single winding on the primary and secondary sides. The primary winding is connected to the source of supply and the secondary winding provides electric power to the load. The windings are placed on a magnetic core which provides a path for the magnetic flux.
Single-Phase CTs are used in power distribution systems for domestic and commercial usage. They are easier to install and maintain.
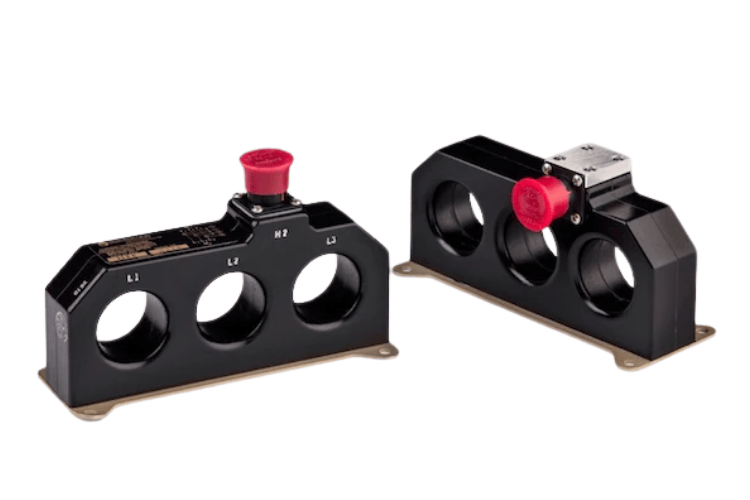
Three-Phase Current Transformers
Three-Phase Current Transformer contains three interconnected single phase transformers in a single housing - created by either using a single 3 phase core or three individual toroidal cores. They are used for measuring or monitoring high currents in three-phase electrical systems. These CTs provide simultaneous current measurements across all three phases, ensuring accurate monitoring and protection of the entire system. They are used in metering, energy management, fault detection, power quality analysis and system stability in complex electrical setups. Their ability to handle high power loads makes them indispensable in industries and power plants.

Current Transformer Types Based on Core Types
Current transformers (CTs) have different core designs that significantly influence their performance, accuracy, and suitability for different applications. Following are the key types of CTs based on their cores.
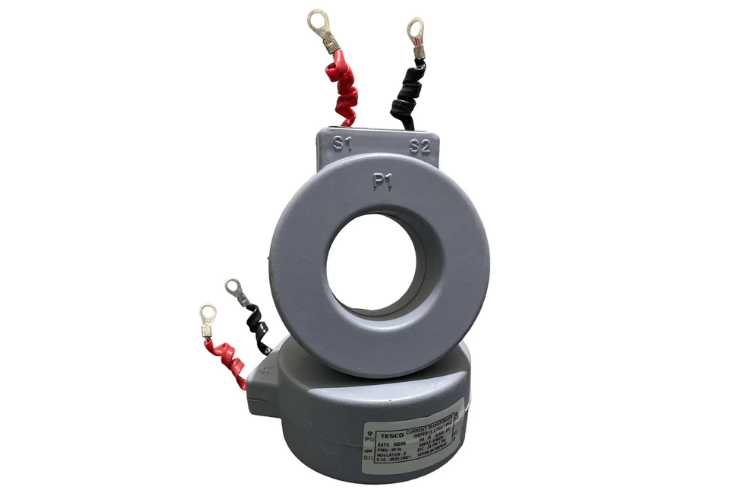
Wound Core Current Transformers
A wound current transformer has the primary winding and a secondary winding wound around the core. This primary winding is connected in series with the conductor and the secondary winding provides a reduced current proportional to the primary current. Wound CTs are used in high-voltage applications where precision and reliability is critical.

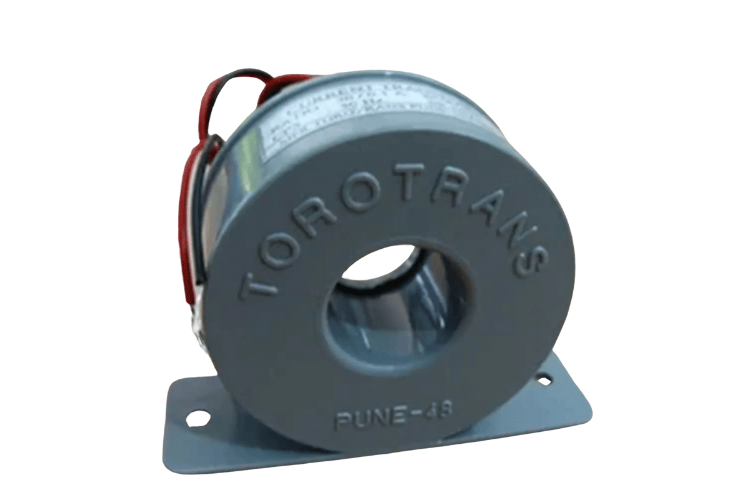
Toroidal (Ring) Core Current Transformers
Toroidal Core Current Transformers have a ring shaped core and the conductor passes directly through the center of the core. They don’t have a primary winding.
Their secondary winding is wound around the core which is made of a magnetic material.
These CTs are compact, easy to install and suitable for low and medium current measurements. They are used for energy monitoring, power quality assessments and load analysis.

Split Core Current Transformers
Split Core Current Transformers have a unique design that allows the core to be split open. They can be clamped around an existing conductor without disconnecting the circuit. This hinged core mechanism makes them suitable for retrofitting applications and temporary setups. Due to the hinged core mechanism, the core can have air gaps which can impact its accuracy. They are commonly used in power operations and electricity reconstruction projects.






